UPnP NAT Router Configurator
These tools have not been in active development for quite some time, but they remain available for as long as they function, and for anyone who wants to play with them.
Current version: 1.2
Two issues to resolve when setting up a home server (after SECURITY) are
- opening up a port in your router/firewall for incoming connections
- knowing and advertising your external IP address (especially when it changes because you rebooted your DSL router
This tool can help with both. A UPnP (Universal Plug-n-Play) enabled router can be provisioned by a Windows program (a process called NAT router traversal). The router can also tell you your external IP address. This program does both of these things for you.
Files: Zip Archive containing both the 32-bit and 64-bit versions with MD5 hash and PGP signature.
Important Info
- This version of the tool was compiled under Visual Studio 2008 (VC9) on Windows 7 Professional. The resulting 32-bit and 64-bit executables were tested on Windows Vista Business 32-bit and Windows 7 Professional 64-bit systems.
- The Windows XP SP3 32-bit system I tried this program on showed some problems. Things that used to work fine do so no longer. I am still tracking down why that is a problem.
- You MUST be running at least Windows XP. The Windows API being used is apparently only available since Windows XP, and even then some things are not so happy making.
- You need a router with Universal Plug-n-Play (UPnP) and to have UPnP enabled.
- Back when I first built this tool it turned out that your system had to be using DHCP (dynamic host control protocol) rather than a static IP address. Othewise the OS would not pass out the information about the mappings. I am uncertain whether that requirement still applies.
Line-item Format
The line-item format is:
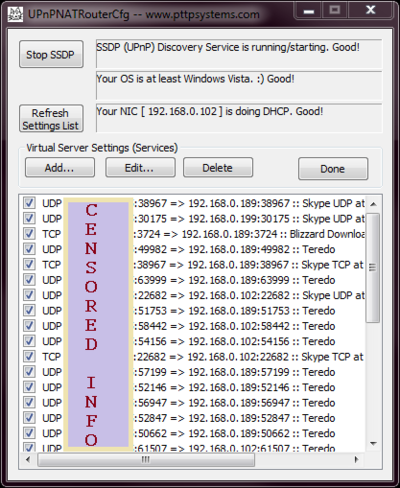
[check] PROTO EIP:ePort =>IIP:iPort :: Name
- [check] is checked if the mapping is enabled
- PROTO is either TCP or UDP for the packet type being mapped
- EIP is the EXTERNALLY VISIBLE IP ADDRESS -- this is what you advertise
- ePort is the external port being mapped
- IIP is the internal IP to route packets to
- iPort is the internal port for the mapping
- Name is the string describing the mapping (what service it supports)
Here is a screen shot. My EXTERNAL IP address is censored for my own safety. :)